If you are reading this, you may have quite a few devices connected to the internet, but have you ever stopped to wonder how your laptop, smartphone, or even smart fridge connects to the internet? It all comes down to something called an
IP Address.
IP addresses are at the very core of how the internet works. They’re the digital equivalent of a return address, making sure information gets to the right place. But here’s the thing, not all IP addresses are the same. There’s a whole ecosystem of IP addresses out there, each with its own unique job to do. And while it might sound like techy mumbo jumbo, understanding the basics can be surprisingly helpful — whether you’re troubleshooting your home Wi-Fi or setting up a new server for your business.
In this guide, we’re breaking it all down for you: the types of IP addresses, what they do, and why they matter. So grab a coffee (or tea, we don’t judge) and let’s dive into the world of IP addresses —
made simple, not scary.
What Is an IP Address, Really? (In Simple Terms)
Alright, so what exactly is an IP address? Let’s start with the basics: it’s a string of numbers (and sometimes letters) that acts like a label for your device on a network.
Think of it as the name tag your device wears to identify itself when it’s online.
Here’s a quick analogy: Imagine you’re at a party, and everyone’s wearing name tags so they can introduce themselves. An IP address works the same way but in the digital world. It lets your device say, “Hi, I’m Device A, and this is where you can find me!”
There are two main kinds of IP addresses you’ll encounter:
- IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4): This is the OG of IP addresses that has been around since the early years of the internet. It uses a 32-bit system, which gives us about 4.3 billion unique addresses. Sounds like a lot, right? But with billions of devices connected to the internet, we’ve actually run out of IPv4 addresses.
- IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6): Enter IPv6, the upgraded version. This bad boy uses a 128-bit system, allowing for an almost infinite number of unique addresses. With IPv6, we’ve sort of future-proofed ourselves for all the smart toasters and AI robots we’ll have to connect to the internet someday.
Both IPv4 and IPv6 do the same basic job: they identify devices and ensure data gets to the right place. The difference is mainly in capacity and efficiency.
Key Features of the IPstack API:
✔️
RESTful architecture – Uses standard HTTP methods (GET)
✔️
JSON responses – Returns structured data in an easy-to-use format
✔️
Scalable & fast – Designed for real-time IP lookup and geofencing
✔️
Supports HTTPS – Included with your paid subscription
Example API Request:
To validate an IP address, you can send a GET request to:
https://api.ipstack.com/134.201.250.155?access_key=YOUR_ACCESS_KEY
Spotlight on Private IP Addresses
Now, let’s talk about private IP addresses. Private IP addresses come into play when devices need to talk to each other within a private network, think of your home Wi-Fi or an office network. They’re specifically designed to work behind the scenes, without being exposed to the broader internet.
For example, when your laptop connects to your printer, it’s using a private IP address.
That’s great but…Why do private IP addresses matter in everyday life
- Local Communication: They let your devices, like your laptop, printer, and smart TV, talk to each other without needing to involve the internet. For example, when you’re streaming a movie from your laptop to your smart TV, that’s private IP magic at work.
- Security: Since private IPs aren’t accessible from outside your network, they provide an extra layer of security. Think of them as a gatekeeper, keeping your local traffic separate from the big, bad internet.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Private IPs are reusable. That means the same address can be used in different private networks around the world without causing conflicts. This helps conserve the limited pool of public IPs.
Why Private IP Addresses Matter In Everyday Life
Imagine if every single device in your home needed a public IP address. That would not only be impractical but also pose significant security risks. Private IP addresses simplify things by allowing devices to communicate locally without exposing them to the internet—keeping your network safer and more efficient.
They’re also vital for conserving the limited number of IPv4 addresses available, ensuring we don’t run out of these crucial resources.
Breaking Down Private IP Address Classes
Let’s talk about private IP address classes. Each class has its own range of addresses and is tailored for specific needs, from massive corporations to cozy home setups. Here’s how they work:
Class A Private IP Address
Range: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
The Class A private IP range is the largest of the three classes. It spans from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255, offering a whopping 16 million-plus unique IP addresses. That’s a lot of room for devices to coexist within one network!
Best Use Cases:
Large organizations or enterprises with thousands of devices on the same network.
Real-World Applications:
Imagine a big tech company like Google. With thousands of devices—from servers to employee laptops—all interconnected, a Class A IP range ensures seamless communication while keeping everything secure and private.
Class B Private IP Address
Range: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Class B private IP addresses occupy a middle ground in terms of size and use case. With a range from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255, this class provides a total of 1 million unique addresses. It’s smaller than Class A but still ample for medium-sized networks.
Suitable For:
Medium-sized networks like schools, colleges, or medium businesses.
Real-World Examples:
Think of a university campus where different departments need their own sub-networks but still want to be part of a larger private network.
Class C Private IP Address
Range: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.25
Perfect for small office/home networks
Class C is the go-to choice for small businesses, home offices, and personal networks. It’s simple to manage and provides enough addresses for most small-scale needs.
Everyday applications you might relate to
You know that WI-FI router you have at home? Chances are, it’s using a Class C IP address to manage your devices. From your smart TV to your laptop, all these devices communicate via this small range of addresses. For example, your router might assign 192.168.0.1 to itself and 192.168.0.101 to your laptop. It’s the go-to range for connecting personal devices like phones, printers, and smart gadgets.
Private vs. Public IP Addresses – A Quick Comparison
Image Description: Private IP addresses vs Public IP addresses
Private vs. Public IP Addresses – A Quick Comparison
Now that we’ve covered private IPs, you might be asking: what’s the difference between private and public IP addresses? Here’s an easy breakdown:
Key Differences Simplified
- Private IPs: These are used within local networks and aren’t accessible from the internet. Think of them like your private phone extension at work.
- Public IPs: These are the addresses visible to the wider internet. They’re like your direct office number, allowing anyone to reach you from anywhere in the world.
When to Use Each Type
- Private IPs: Ideal for internal communication, like connecting your devices at home or within an office. They’re secure, reusable, and don’t take up valuable public IP space. Essentially, If you own a router, you would already have a private IP address that’s working for just you, your network and your router.
- Public IPs: Necessary when you want devices to communicate directly with the internet. For example, websites, email servers, and gaming servers need public IPs so users around the globe can connect. Your public IP address works as a passport to the internet, you couldn’t access much online without one!
Keep In Mind: You already have both a public and a private IP address!
How to Find Your Own IP Addresses (Public and Private)
Finding your public and private IP address is pretty straightforward. You can usually find your public IP address through sites like
IPstack (clicking the “Find IP Location” button). To find your router’s private IP address, you can take a look at your device’s system settings. The steps may vary on whether you’re using Windows, MacOS, IPhone, or Android but they are all just as easy! We have listed the easiest way to find your private IP addresses for each device below!
Knowing your IP can help with troubleshooting, setting up devices, or just satisfying your curiosity!
How to Find Your IP Address using IPstack API
Looking for an easy way to find your IP address?
IPstack API makes it simple! Just follow these steps:
- Sign up for IPstack API – Head over to the IPstack website and create a free account.
- Get your API Key – Once you’re signed in, navigate to the dashboard and copy your unique API key.
- Make an API request – Open your browser or use a tool like Postman and enter the following URL.
https://api.ipstack.com/check?access_key=YOUR_ACCESS_KEY
In the URL, make sure you replace “YOUR_ACCESS_KEY” with the API key from the dashboard
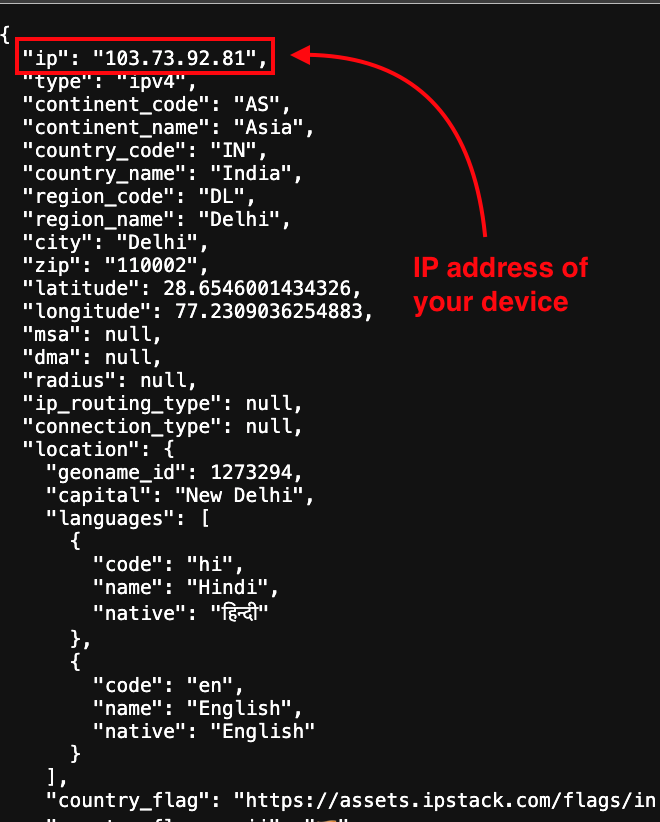
- Check the response – The API will return a JSON response. Look for the “ip” field, and voilà—that’s your public IP address!
How to Find Your IP Address Using Windows
- Click start OR press the Windows button on your keyboard, then click Settings.
- Click On the Network and Internet tab.
- Click On Properties
- Look for your IPv4 address. This number is your local IP address.
There’s an even quicker way to do it on Windows that we thought was worth mentioning!
- Click start OR press the Windows button on your keyboard, then click Settings.
- Type “cmd” then open the Command Prompt window
- As soon as you’re in the command prompt, just type “ipconfig” then press enter
- Scroll and find “IPv4 address”. That is your local IP address.
How to Find Your IP Address Using MacOS
If you are looking for your private IP address on Mac, just follow these simple instructions below:
- Open the Launchpad and select System Settings (might be called System Preferences)
- Click on the Network tab
- Choose your network connection from the menu (Example Wi-Fi with connected symbol)
- Click on Details tab
- You will see your local IP address listed next to IP Address and underneath your router IP address
How to Find Your IP Address Using IPhone or IPad
If you are looking for your private IP address on your IPhone or IPad, just follow these simple instructions below:
- Go to Settings.
- Tap Wi-Fi
- Tap the information icon next to your Wi-Fi connection. Scroll until you see your default IP address under the “IPV4 ADDRESS” section
How to Find Your IP Address Using Android
If you are looking for your private IP address on your Android device, just follow these simple instructions below:
- Go to Settings.
- Press About Phone
- Press Status Information. You will see your IP addresses listed.
FAQs About IP Addresses
Can private IP addresses be used on the internet?
If a private IP address is used on the internet, it won’t be recognized because routers block private IP ranges from being routed externally. Instead, NAT (Network Address Translation) converts private IPs into public ones for internet access.
How do I find my private IP address?
On Windows, open Command Prompt and type
ipconfig. On macOS, go to System Preferences > Network.
What’s the difference between a private and a public IP address?
A private IP address is used within a local network (e.g., home Wi-Fi), while a public IP address is assigned by your ISP and allows devices to communicate over the internet.
Can I change my private IP address?
Yes! You can change your private IP address by rebooting your router or manually assigning a new IP in your device’s network settings.
Why do routers use private IP addresses?
Routers assign private IP addresses to connected devices to efficiently manage traffic, enhance security, and conserve public IPs through NAT (Network Address Translation).
Can two devices have the same private IP address?
Yes, but only if they are on separate networks. Within the same network, IP conflicts occur if two devices have identical private IPs.
How does IPstack help businesses with IP addresses?
IPstack provides real-time IP geolocation, fraud detection, and network insights to help businesses personalize user experiences, enhance security, and optimize traffic routing.
What happens if I use a private IP address on the internet?
If a private IP address is used on the internet, it won’t be recognized because routers block private IP ranges from being routed externally. Instead, NAT (Network Address Translation) converts private IPs into public ones for internet access.
Are private IP addresses unique?
Private IP addresses are unique
within a local network but can be reused in different networks. That’s why multiple homes or businesses can have devices using
192.168.1.1 without conflict.
Why are private IP addresses important for cybersecurity?
Private IPs add an extra layer of security because they are not directly accessible from the internet. This reduces the risk of cyber attacks and unauthorized access to your local network.
Do mobile devices use private IP addresses?
Yes! When connected to Wi-Fi, mobile devices use a private IP address assigned by the router. However, when using cellular data, they typically use a public IP assigned by the mobile carrier.